VERB
The verb is one of the parts of speech. It helps us in many ways. The verb tells us about -
- An action
- An occurrence
- A state
- The tenses
- The mood in a sentence
- Main verb/Principal verb/Lexical verb
- Action verb/Dynamic verb
- Non-action verbs/Stative verb
- Linking verb
- auxiliary verb/helping verb
- Primary Auxiliary
- to-be form
- to have form
- to do form
- modal auxiliary
- You played football. (Past Tense) (2nd person)
- I play football. (Present Tense) (3rd person)
- He plays football. (Present Tense) (3rd person) (singular)
- Rohit thinks to correct his previous mistakes. (Present Tense) (3rd person) (singular)
- Rohit thought to correct his previous mistakes. (Past Tense)
- They think to correct his previous mistakes. (Present Tense) (3rd person) (singular)
- This soup tastes sweet. (Present Tense) (3rd person) (singular)
- This soup tasted sweet. (Past Tense)
- He is a teacher. (Present Tense)
- He was a teacher. (Past Tense)
- to-be form- is, are, am, was, were, will be, shall be.
- to have form- has, have, had
- to do form- do, does, did
- will, would, can, could, shall, should, may, might, must, aught to, need, dare, used to.
- Dinesh can drive all four-wheelers. (Present Tense)
- Dinesh could drive all four-wheelers. (Past Tense)
- You were playing in the garden. (Past Tense)
- she was playing in the garden. (Past Tense)
- I am playing in the garden. (Present Tense)
1. She doesn't sing in front of her teachers.
2. Vedhant likes eating traditional food.
3. You visited Udaipur twice.
4. I is a big green meadow.
5. Rose smells nice.
6. Divya has completed her project.
7. All the beggars had gathered at rest house before Rakesh house.
8. You have repaired my mobile.
9. All the children are making noise.
10. They love drinking milk.
11. She feels cold.
12. Suman believes in saving.
13. Radha threw a ball.
14. Rohit can mend computer.
15. We are Indians.
16. Students purchased new books.
17. Rohan threw a ball on me.
18. She cleans utensils.
19. The gardener plucks the flower.
20. Students came to school yesterday.
21. They pluck flowers in the morning to sell.
22. You hanged this poster in drawing room.
23. He will be in Delhi next week.
24. I am enjoying the show.
25. We have donated all the books.
26. Vikas does not help others.
27. The shopkeeper is selling fresh fruits.
28. I have a smart phone.
29. I own Shri Ramcharitr Manas.
30. I prefer coffee to tea.
31. Deepak seems weak.
32. My mother tasted the porridge.
33. I am the monitor of the class.
34. Mr. Mehta was a manager in this bank.
35. The elderly man might enjoy rock show.
36. I will buy chocolates for you.
37. They have a plan.
38. He gifted Suresh a shirt.
39. My mother bought a laptop.
40. I am a doctor.
41. Shopkeeper offered me a discount.
42. Our gate keeper was upset yesterday.
43. Everybody respects teachers.
44. She doesn't sing in front of her teachers.
45. Vedhant likes eating traditional food.
46. It is a big green meadow.
47. Rose smells nice.
48. You see problems with that.
49. You are gorgeous.
50. We think that the show is great.
51. The food tastes good.
52. My teacher offered me a scholarship.
53. My mother cooked food for me.
54. My mother is very lovely.
55. Our principal is very strict.
56. The weather was very cold.
57. Flower smells sweet.
58. Yesterday, apple Ice-cream tasted delicious.
59. I cut all the fruits.
60. They laugh loudly.
61. We watered the plants in the evening.
62. She cooks delicious food.
63. The cat jumped in the well.
64. You throw stones in the pond.
65. I sweep the room.
66. You must come to school in uniform.
67. He could manage his funds by himself.
68. You must have appeared in the examination.
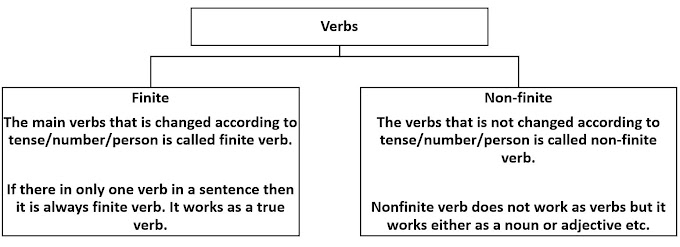
The verb that does not indicate tense, person, or number is called a nonfinite verb. It may work as a noun or adverb or adjective but not as a verb that's why it is also called a pseudo-verb/false verb.
Any action and stative verb can be a nonfinite verb if it is not changed according to the tense of the sentence or the number of the subject (singular/plural) or the person of the subject (first, second and third).
- She goes to the market to buy clothes. (1st form)
- They went to the market to buy clothes. (1st form)
- We go to the market to buy clothes. (1st form)
- Dinesh goes to the market with a broken helmet. (3rd form)
- You went to the market with a broken helmet. (3rd form)
- You go to the market with a broken helmet. (3rd form)
- My brother goes to the market taking flower baskets. (....ing form)
- They went to the market taking flower baskets. (....ing form)
- We go to the market taking flower baskets. (....ing form)
'taking' does not change according to tense /subject/number; hence it is non-finite here.
EXERCISE.
Q1. Underline all the verbs in the given sentences and identify finite and nonfinite verbs-.
- Being ill, Nidhi is not going to school.
- A day without sunshine is cool.
- Ayushi likes walking in her garden.
- Both of us will reach the theatre before the end of the drama.
- The hungry Babita ate a large dinner.
- Daksh watched a wounded bird.
- We completed our homework after school.
- she was telling the funniest joke after attending the evening session.
- I slept after working all day.
- Turning to the left, you can see a big Haveli.
- I ordered traditional delicious food to impress his boss.
- Vikrant waited for the train after reaching the platform.
- My sister and mother took the bus.
- Varun had already seen that ruined building.
- We were playing in the garden when the guests arrived.
- You shouldn’t have done this to me.
- She leaned out of the window to call her friend.
- You don’t look happy to see me.
- In the evening, I will go to the market.
- I will join you soon at the meeting.
Q2.
Find finite and nonfinite verbs in the following sentences
1. I like solving problems in Mathematics.
2. Rohit was very bad at gardening.
3. The man sitting over there is my elder brother.
4. Broadly speaking, the project was successful.
5. He had three things taken away from him.
6. I visited the temple to pray load Shiv ji.
7. Disha found her lost purse.
8. I aim to convince him of our plan’s ingenuity.
9. I can sit here all-day
10. You can’t make this pot.
Q3. Find whether the bold words are finite or
nonfinite verbs-
1. We found him smoking behind the shed.2. They have run away together.3. Nancy does her homework every day4. They are writing a letter.5. She tried to help him6. It is healthy to laugh at problems.7. Finding the gates widely open, the thief went inside8. He was wearing a torn shirt.9. He is about to leave.10. Students leave the class at 3:00 PM.