Age is no bar for learning and sharing. This blog will definitely develop your skills -reading , writing, listening, speaking, reasoning etc. Subject related written content, stories as well as videos imbedded in the content page will assist you to be confident enough to face challenges in real situations in life.
Thursday, December 23, 2021
Previous year question papers | BCA| CCS University | BCA-I year questio...
Friday, December 3, 2021
PHONETICS
1. 1. Phonetics
2. Syllables
a. Structure of syllables
b. Types of syllables
i. Monosyllabic words
ii. Disyllabic words
iii. Polysyllabic words
· Tri syllabic words
· Quadra syllabic words
· Penta syllabic sentences
· Hexa syllabic words
4. Graphemes
5. Morphemes
6. Allophones
7. Stress
WRITING
- Writing skills
- Notice Writing
- Poster Writing/making
- Message Writing
- Advertisement Writing
- Letter and it's types
- Formal Letter Writing
- Types of Letters
- Business Letter
- Business Letter: Structure
- Business Letter: Formats
- Business Letter Writing Process
- Business Letter Function
- Business Letter Types
- Official Letter
- Demi Official Letter
- Memorandum Writing
- Note Making
- Applications to Principal
- Letters to Authorities
- Letters to Editors
- Informal Letter Writing
- Diary Entry
- Report Writing
- Proposal Writing
a. Job Application Writing
b. Resume Writing
c. Biodata Writing
- Technical Paper Writing
- Scientific Paper Writing
a. Sales letterb. Enquiry letterc. Quotation letters (Replies to Enquiry letter)d. Order lettere. Complaint letterf. Adjustment letterg. Circular letterh. Letter for application of agency
LITERATURE
- Ballad
- Dramatic Monologue
- Elegy
- Epic
- Lyric
- Ode
- Sonnet
- To Sleep -John Keats
- Palanquin Bearers- Sarojini Naidu
- Three Years She Grew- William Wordsworth
- Rugby Chapel-Mathew Arnold-Questions
- Rugby Chapel-Explanation (Hindi & English)
- En Elegy Written In Country Churchyard-Thomas Gray
- We Are Seven-William Words Worth
- The renunciation
- The Gift of Maggi
- Ruskin Bond: The Eyes Are Not Here
Thursday, December 2, 2021
COMMUNICATION: LEVELS
LEVELS OF
COMMUNICATION
We live in society and being a
social animal, we need to talk to various people to satisfy our needs. Sometime
we talk to either ourselves or animals or to others for satisfying our needs.
It means we talk for different people on different levels. There are five
levels of communication.
1. Extra personal:
-Communication between human beings and non-human entities is called extra
personal communication. This form of communication requires more perfect
co-ordination and understanding between the sender and the receiver. At least
one of them either transmits information or responds in sign language. When you
return from your office your dog comes to you and wage his tail. You
immediately grab him in your arms and start talking to him and he responds in
sign language but you understand and communication goes on.
2. Intra personal: - this
takes place within the individual. The brain of a person is linked to all the
parts of the body by an electrochemical system. Any organ behaves like sender,
electrochemical impulse is message and the brain is receiver and then brain
acts as sender and sends feed back to the organ which bow acts as receiver.
This communication pertains to thinking self-motivation, self-determination etc.
lake place at the intra-personal level.
3. Interpersonal: - In
this level sharing of information among people is started. It differs from
other forms of communication in the way that at least two people are involved
in it. The speaker and the listener are in close physical proximity to each
other, there are no sensory channels are used and feedback is immediate. It is
advantageous as feedback is direct and immediate. Nonverbal plays a major role
in this communication due to proximity of the people involved. This
communication can be formal or informal. Interpersonal communication situations
depend on a variety of factors: - psychology of two parties, relationship
between them, situation, environment and cultural context. Whenever both the
parties have some common frame of reference, background, purpose and interest
they have relevant interaction. If anyone party is not interested, no
communication takes place. If a person is instructing to his junior and he
understands the thing and responds accordingly it means the interpersonal
communication is effective and fruitful.
4. Organizational
communication: - This type of communication takes
place in an organization at different hierarchical levels. It makes the
functioning of an organization smooth. It plays an important role in the growth
of organization. The different hierarchical levels are
a) Internal-operational: - It helps in conducting smooth functioning within an organization.
b) External-operational: - It helps in making communication outside the organization for a specific purpose.
c) Personal: - Communication that occurs among the workforce without a purpose related to business or job is called personal (organizational) communication.
5. Mass communication: - The communication through which we can spread our message to a large number of audiences at one time is called mass communication. Either a person or an organization or a group acts as sender and a number of people are there at the receiver end. In this type of communication, we require a mediator to transmit the information. There are several example of mass media such as journals, books, television and newspapers. A
ll these media mediate such communication.
This is more persuasive than any other form of communication. It requires
utmost care on the part of the sender in encoding the message. Some equipment
are required in oral communication and print or visual media.
Its main characteristics are
a) Large
reach: -It has large reach as one person can send his
message to countless people at a time.
b) Impersonal: -Mass
communication is impersonal in its services. It delivers the message to all
without biasness.
c) Presence
of gate keeper: - Mass communication needs additional persons,
institutions or organization to convey the message. Gate keeper may be a person
or active group. Example editor is the gate keeper in the mass
communication.
COMMUNICATION: FLOWS
FLOWS IN
COMMUNICATION
Information
follows in an organization both formally and informally. The spread of
information helps organization to coordinate with others internally or
externally. Information is flew in an organization in two ways formally and
informally. On that basis flows in communication are of two types-
1. Formal flow
2. Informal flow
1. FORMAL FLOWS
The term formal
communication refers to communication that follows the official hierarchy and
is required to do one’s job. Internal operational and external operational
communication can be described as formal. Information of various kinds flowing
through formal channels, such as policy or procedural changes, orders,
instructions, etc.
Importance/merits/advantages
v It is authenticated and systematic hence it can be relied.
v It is helpful in coordination and maintaining discipline in an organization.
Demerits/disadvantages
v It follows rule hence it is slow in speed.
v It stops open flow of communication
v Various organizational barrier may arise at different points.
This type of
formal communication flows in various directions as downward, upward, diagonal,
horizontal.
1. Vertical flow: When two people communicate to each other and they are at different level in an organization then the flow is called vertical flow. The communication between senior to junior or junior to senior comes under this flow. Vertical flow is of two type.
1.A - Vertically Downward communication: - it flows from a manager, down the chain of command. When managers inform, instruct, advice, or request their subordinates, the communication flows in a downward pattern. This is generally used to convey information, new policies or procedures, to seek clarification, to ask for an analysis etc. Superiors send feedback about their subordinates’ action through this channel. Such communication increases awareness about the organization among subordinates and employees and enables managers to evaluate the performance of their subordinates. Examples: - memos, notices, face to face interactions, or telephone conversations.
Importance/advantages/merits:
v Controls working environment and discipline
v Orders, instructions, directions, promotion, guidelines, appreciation, punishment etc. are given
v Explaining complex issues to juniors
Disadvantages/demerits:
v It encourages fear.
v May check open communication environment
v It promotes Authoritative behavior.
v It suppresses the upward communication.
1.B- Vertically Upward communication: - When subordinates send reports to inform their superiors or to present their findings and recommendations the communication flows upward. Seniors make decisions and problems are solved with the help of this communication. The extent of upward communication depends on the organizational culture. In an open culture without too many hierarchical levels, managers are able to create a climate of trust and respect and upward flow is enough. In a highly authoritative environment, where downward flow dominates, upward communication is limited.
Importance/advantages/merits:
v Feedback helps in development of planning
v Request are made
v Message is delivered/Information is passed
v Promotes harmony.
v For registration of grievances
Disadvantages/demerits:
v It encourages flattery.
v May risk discipline.
v May be manipulated due to fear of superiors
2. Lateral or horizontal communication: -
This form of communication takes place among peer groups (same level people) or hierarchically equivalent employees. Such communication is often necessary to facilitate coordination, save time, and bridge the communication gap among various departments. This communication can be advantageous or disadvantageous. It is very vital for the growth of an organization as it builds cooperation among the various branches. In organizations where work is decentralized, it plays a greater role because there is a higher probability communication gaps.
Importance/Merits:v In making decision
v For discussing important points
v For making policies, rules, upcoming suggestions etc
Demerits:
v Ego of the persons at the similar level.
v Clashes related to ideology.
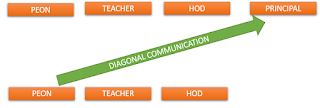
3. Diagonal or cross-wise communication or radial: - diagonal communication flows in all directions and cuts across levels in an organization. When a sales manager communicates directly with the vice president they are engaged in diagonal communication. Though it deviates from the normal way but it is quick and efficient. The increase use of e-mail also encourages cross-wise communication. It is also called radial or circular communication as there is no specific line of command.
Importance/merits/advantages
v It saves time.
v Reduces barriers.
v increases the efficiency
v Uses as team build up/motivational tool.
Demerits/disadvantages
v increases competitiveness
v Gives threat to discipline
v Gives threat to coordination
v Creates internal disorder
v Bad effect on formal relations
INFORMAL FLOW
(GRAPEVINE)
Upward, downward,
horizontal and diagonal flow is the need of an organization because these flows
run formally. Other than formal channel there is one more channel which flows
the information without considering the direction in an organization. This
informal flow is called grapevine. It is found in every organization. It is
unwanted by the authorities but it grows like weed. This channel grows wild and
it spreads information unofficially. It is also proved that grapevine is
important source of information that supplement official channel. Grapevine is non-directional
and it can enter at any point in the process of communication. Sometimes
managers used grapevine in a smart way to spread the information in a short
time.
Grapevine is an
informal channel of business communication. It is called so because it
stretches throughout the organization in all directions irrespective of the
authority levels. It grows when people start interaction in an organization. It
exists more at lower levels of organization. Thus, grapevine spreads like fire
and it is not easy to trace the cause of such communication at times.
Reasons of grapevine
Grapevine
generally develops due to various reasons.
v Uncertainty during recession.
v Lack of self-confidence due to which employees form groups or unions.
v Bias attitude of seniors
v Development of informal relation among co-workers
v Changes in position, policies, promotions, demotions, transfer etc.
Ways to make Grapevine Beneficiary to Organization
v Providing real news to the grapevine initiators.
v Creating positive messages for grapevine
v Contradicting the false rumor.
v Allowing workers in the decision-making process
v Developing a good organizational climate.
Advantages of Grapevine Communication
v Grapevine channels circulates information rapidly.
v Feedback is quick as compared to formal channel of communication.
v grapevine helps in developing group cohesiveness.
v It becomes the tool of stress buster.
v It serves as an emotional supportive tool.
v It reaches to every hook and corner where formal communication cannot reach.
Disadvantages of Grapevine Communication
v It is incomplete as it is more based on rumours.
v It is not trustworthy always as it does not follow hierarchy and is spread more by gossips and unconfirmed sources.
v It may reduce the productivity of employees as they spend more time talking rather than working.
v Negative grapevine damages the reputation of an organization.
Types of grapevine
a) Single Strand Chain: In single strand chain one person pass message to only second person then second person this information to the third person and it goes on.
b) Gossip Chain: In the gossip chain, one person remains in the center and passes information to everyone nearby.
c) Probability Chain: The probability chain is a random process in which someone transmits the information to others without targeting the recipient.
d) Cluster Chain: In the cluster chain, a person tells the information to the selected people who may in turn pass the information to other selected people. Here, recipient is the selected person.