COMMUNICATION
Since, the dawn of the civilization, communication has been the only way to connect people with each other. In daily life, people share number-less ideas, information, feelings etc. to each other and for this purpose they need to communicate in different ways.
Definition
1. According to the Oxford Advanced Learner’& Dictionary-
‘communication’ means the activity or the process of expressing ideas and feelings or information.’
2. According to Koontz and O’Donnel-
Communication may be understood “as the exchange of information at least between two persons with a view to create an understanding.......”
The word 'communication' is derived from a Latin word ‘communicare’ which means to share/transfer of data, or information. Hence, we can say that communication is the process of transferring of an idea, knowledge, information, feeling, thoughts, or news from one person to another. Communication involves (at least) a sender, a message and a recipient. It also includes our emotions, cultural situation, the medium used to communicate, etc.
It is a two-dimensional, dynamic and interactive process. It is interactive because at least two individuals (or two body parts in case of intra-personal personal communication) take part actively to develop understanding between them. It is dynamic because; it is not passive and does not happen just like that. It includes a variety of forces and activities interacting over time;
Communication is done if there are three things-
1. Specific subject matter (message)
2. specific purpose
3. specific receiver (reader/listener)
FIELDS OF COMMUNICATION
1. GENERAL COMMUNICATION
In our daily life when we talk to each other casually, we do General Communication. We use General communication with our relatives, friends and family members. Even we do general communication with our colleagues in our professional life. We transfer information related to non-professional life, we share our feelings and emotions.
2. TECHNICAL COMMUNICATION
General communication means transfer of general ideas or views or feelings from one person to another but when we talk about technical Communication it means transfer of technical information from one individual or group to a targeted audience.
According to the Oxford Advanced Learners Dictionary ‘technical’ word means connected with the practical use of machinery, process etc. in science and industry.
Hence, Technical communication means the transmission of fact, figures, ideas (all sorts of scientific and technical information) from one individual to another. It adopts all the methods like media, networks, channels and systems for communication. Technical communication may vary from a simple description of a tool to a very complex explanation (in simple language) of a scientific research. Some examples of Technical Communication are seminars, reports, research projects, meetings etc.
3. PROFESSIONAL COMMUNICATION
Professional communication means transfer of information, data, message etc from one professional to a concerned receiver. Professional communication is related to one's profession. If someone is related to any profession, no matter big or small, he automatically uses professional communication for solving different problems, or giving suggestions, or making relations, or passing information etc. Technical as well as professional communication is formal in nature and both help the professionals either in one way or the other. Some examples of professional communication are letters, notices, memos, presentation, reports, proposals etc.
4. BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
Business communication means 'transfer of message from one business person to a targeted receiver'. A businessman and associated employees use business communication to run a business smoothly and build its relation with stakeholders. Some examples of business communications are sales letters, order letters, proposals, tenders, presentation, press release etc.
DIFFERENCES
BETWEEN CONVERSATION AND COMMUNICATION
Remember, Conversation is different
from communication.
1. CONVERSATION
a) No specific purpose
b) No specific audience
c) No specific subject matters
d) Informal/objective/personal style
e) Local language/dialect is used
f) Facts and data are not mentioned
2. COMMUNICATION-
a) Specific purpose
b) Specific audience
c)
Specific subject matter
d)
Formal/Subjective/Impersonal style
e) Simple and Formal language is used.
f) Facts and data are important to be
mentioned.
Example Of Conversation &
General Communication 1. Conversation- In conversation there is no specific
purpose, specific subject matter and specific receiver. For example- if you are going out for a walk and suddenly you meet an old
friend coming towards you. You start talking to him without predefined
purpose and without a specially prepared message. In this case you have- a)
no specific receiver- it may be any
friend b)
no specific purpose- sudden meeting c)
no specific message (subject
matter)- unplanned talking 2. GENERAL COMMUNICATION- In General Communication there is a
specific purpose, specific subject matter and specific receiver though it is
related to our general life. For example- your father told you to go to your uncle's house and delivered
a message to him to come to your home at 5:00 pm. In this case, you have- a)
a specific receiver- your uncle b)
specific purpose- sending message to
your uncle c) specific message (subject
matter)- inviting uncle at 5:00 pm at your home.
|
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN
GENERAL COMMUNICATION AND TECHNICAL/PROFESSIONAL/BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
1. General Communication-
a) Used for sharing feeling and emotions
b) The purpose is general.
c)
Day to day language/dialect
d) Personal/informal/objective style
e) Oral (face to face/ distant mode)
method
f) Used
among relatives/friends/people nearby
2. Technical/Professional/Business
communication
a) For sharing specific subject matter
(related to field)
b) Purpose is specific-
instruction/direction/order/request etc.
c)
Specific language (related to a particular
field)
d) Impersonal/Informal/Subjective style
e) Generally, rely on written
documents/method
f) Used
among specific audience (related to specific field)
|
BASIS
|
G C
|
TC/PC/BC/
|
|
1. Subject matter
|
general
|
Specific
|
|
2. purpose
|
general
|
specific
|
|
3. Audiences
|
Not always specific
|
Specific audience
|
|
4. Style
|
Personal, poetic, decorative, bombastic
|
Impersonal, Accurate, simple, precise (depends on requirement)
|
|
5. Base
|
May not be factual
|
TC is based on facts
|
|
6. Nature
|
Objective and subjective
|
Objective
|
|
7.Organization
|
Not always structured
|
Well structured / organized)
|
|
8. Techniques
|
Not always specific,
|
Specific techniques are used depend on requirement
|
|
9. Use of graphics
|
May or may not involve
|
Graphics and charts are used
|
|
10. Vocabulary
|
General, use of dialect
|
Should be up-to-date, simple
|
|
11. Contents
|
Informal & sometimes Formal
|
Mostly formal
|
|
12. Language
|
Figuristic, with poetic devices, use of figure of speech
|
Should be simple and easy to understand
|
|
13. Jargons
|
Are not used generally
|
Used
|
|
14. Examples
|
Dramas, novels, Fictions, literature etc.
|
T. reports, Proposals, business letters, news letters etc.
|
|
15. Required for
|
entertaining, passing time, releasing stress, boosting
relation etc.
|
Sharing information, energizing business relations,
increasing business, to instruct etc.
|
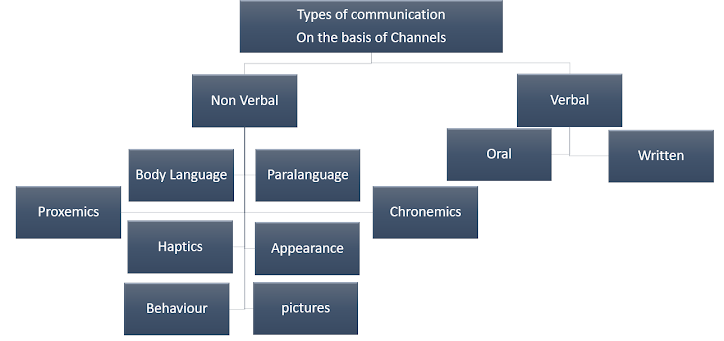
1.
Nonverbal -
a) Use of body and behavior- facial
expressions, eye movements, gesture, posture, touch, etc.
b) Use of voice- cries, screams, howling
etc.
c) Use of noise – drum beating, thumping
of ground, striking of logs.
d) Use of signs- smoke, signs, painting
etc.
2.
Verbal- use of language
a) Oral (speech)
b) Written
MEDIUMS USED FOR COMMUNICATION:
a) face to face
b) animals, birds, smoke, thumping of
ground etc.
c) postal services,
d) telephonic services,
e) internet services,
f)
mass media